Key FPQ-6 Mission Activity
| Revision as of 06:13, 19 February 2007 (edit) Paul (Talk | contribs) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 06:18, 19 February 2007 (edit) Paul (Talk | contribs) Next diff → |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| A full catalogue of Carnarvon FPQ-6 tracking would be a potted history of US space exploration post Mercury. The following group examples pinpoint highlights of Carnarvon’s radar activity in order of the first track in each group. | A full catalogue of Carnarvon FPQ-6 tracking would be a potted history of US space exploration post Mercury. The following group examples pinpoint highlights of Carnarvon’s radar activity in order of the first track in each group. | ||
| - | + | [[Image:Echo.gif|left|thumb|Echo passive communications satellite: Image - NASA]] | |
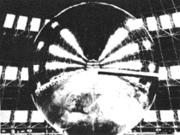
| - | ; '''Communications satellites''' :[[Image:Echo.gif|left|thumb|Echo passive communications satellite: Image - NASA]] Echo-2, a rigidized 30.5m passive communications sphere, launched on 25 January 1964 was the first object in space tracked by Carnarvon. It was followed soon after on 19 August by Syncon-3, the first truly synchronous communications satellite. | + | ; '''Communications satellites''': Echo-2, a rigidized 30.5m passive communications sphere, launched on 25 January 1964 was the first object in space tracked by Carnarvon. It was followed soon after on 19 August by Syncon-3, the first truly synchronous communications satellite. |
| - | ; : Three communications satellites vital to NASA’s communications with its remote tracking stations followed. Intelsat-2A failed to reach a synchronous orbit but before it decayed managed to relay the first few minutes of TV transmission form Carnarvon to England as [[Down Under Comes Up Live]] on 26 October 1966. Intelsat-2B followed on 11 January 1967 to become Pacific-1 – Carnarvon’s communications satellite link to the US. Intelsat-2C on 23 March 1967 became Atlantic-1. | + | ; : Three communications satellites vital to NASA’s communications with its remote tracking stations followed. Intelsat-2A failed to reach a synchronous orbit but, before it decayed, managed to relay the first few minutes of the first TV transmission from Carnarvon to England on 26 October 1966 - [[Down Under Comes Up Live]]. Intelsat-2B followed on 11 January 1967 to become Pacific-1 – Carnarvon’s communications satellite link to the US. Intelsat-2C on 23 March 1967 became Atlantic-1. |
| ; :The SKYNET-1A UK military communications satellites was successfully placed in synchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean on 22 November 1969. SKYNET-1B on 19 August 1970 failed due to a faulty apogee motor and SKYNET-2A launched in January 1974 became lost and shortly after was discovered in a lower Earth orbit by Carnarvon from which it could not be rescued. | ; :The SKYNET-1A UK military communications satellites was successfully placed in synchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean on 22 November 1969. SKYNET-1B on 19 August 1970 failed due to a faulty apogee motor and SKYNET-2A launched in January 1974 became lost and shortly after was discovered in a lower Earth orbit by Carnarvon from which it could not be rescued. | ||
| ; :Telesat-A, a Canadian domestic communications satellite launched on 9 November 1972, failed to reach the correct orbit; nevertheless, Carnarvon, acquiring it a little behind schedule, was able to generate new tracking parameters to enable successful acquisitions by both Hawaii and Bermuda. The satellite subsequently established a successful synchronous orbit. | ; :Telesat-A, a Canadian domestic communications satellite launched on 9 November 1972, failed to reach the correct orbit; nevertheless, Carnarvon, acquiring it a little behind schedule, was able to generate new tracking parameters to enable successful acquisitions by both Hawaii and Bermuda. The satellite subsequently established a successful synchronous orbit. | ||
Revision as of 06:18, 19 February 2007
- Antenna structure
- Tracking and Ranging
- Brief system details
- RCA Computer
- Key Q6 Mission Activity
- Research activity
- BDA, CRO & RCA: Q6 partners
- Other Q-6 tales
Back to Station Equipment
A full catalogue of Carnarvon FPQ-6 tracking would be a potted history of US space exploration post Mercury. The following group examples pinpoint highlights of Carnarvon’s radar activity in order of the first track in each group.
- Communications satellites
- Echo-2, a rigidized 30.5m passive communications sphere, launched on 25 January 1964 was the first object in space tracked by Carnarvon. It was followed soon after on 19 August by Syncon-3, the first truly synchronous communications satellite.
- Three communications satellites vital to NASA’s communications with its remote tracking stations followed. Intelsat-2A failed to reach a synchronous orbit but, before it decayed, managed to relay the first few minutes of the first TV transmission from Carnarvon to England on 26 October 1966 - Down Under Comes Up Live. Intelsat-2B followed on 11 January 1967 to become Pacific-1 – Carnarvon’s communications satellite link to the US. Intelsat-2C on 23 March 1967 became Atlantic-1.
- The SKYNET-1A UK military communications satellites was successfully placed in synchronous orbit over the Indian Ocean on 22 November 1969. SKYNET-1B on 19 August 1970 failed due to a faulty apogee motor and SKYNET-2A launched in January 1974 became lost and shortly after was discovered in a lower Earth orbit by Carnarvon from which it could not be rescued.
- Telesat-A, a Canadian domestic communications satellite launched on 9 November 1972, failed to reach the correct orbit; nevertheless, Carnarvon, acquiring it a little behind schedule, was able to generate new tracking parameters to enable successful acquisitions by both Hawaii and Bermuda. The satellite subsequently established a successful synchronous orbit.
- By mid 1997 535 domestic communications satellites had been launched. About 50 of these would have been supported by Carnarvon before its FPQ-6 ceased tracking in mid-1975
- Apollo/Saturn
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- Ranger
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- Gemini/Agena
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- Pioneer
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- Surveyor
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- Lunar Orbiter
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- WRESAT
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- OV series
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- Skylab
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space
- AE-C
- watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space watch this space